By: Stephen Angeloni, PhD, Sr. Field Application Scientist, Luminex
From streamlining your workflow to general troubleshooting, learn the benefits and the mystery behind xMAP® Microspheres
Curious about the technology driving your life science testing processes? Discover the unique features of our bead products with their ability to enhance and simplify your workflow, revolutionizing how you perform multi-analyte analysis.
The key to simplifying how you perform efficient multi-analyte analysis is with our xMAP® microspheres (aka beads). xMAP® beads make our technology a one-of-a-kind platform. So, what are they? xMAP beads come in two forms:
- MicroPlex® beads are polystyrene particles with a uniform diameter of 5.6 µm.
- MagPlex® beads are 6.5 µm in diameter. MagPlex beads are derived from the standard polystyrene microspheres used to make MicroPlex beads but are coated with iron to provide them with superparamagnetic particle-like characteristics.
Both bead types are coated with carboxyl groups allowing proteins or amine modified oligos to be coupled to the beads for the development of different proteomic or nucleic acid applications. The small size and density of both bead types allow the beads to stay in suspension resulting in fast and more complete interactions with analytes in samples.
Streamline your multiplex workflow with xMAP beads
MicroPlex beads are internally dyed with different concentrations of two dyes, enabling Luminex to make 100 different types of beads with slightly different colors.
MagPlex beads are internally dyed with different concentrations of up to three dyes, enabling Luminex to make 500 distinctly colored bead sets. The superparamagnetic properties of MagPlex beads allow them to move quickly in a magnetic field and re-suspend easily upon magnetic field removal. This eliminates the need for centrifugation or filtration steps during assay development and processing.
With both bead types, the power of multiplexing allows the development of assays that require less sample and fewer reagents to yield more data faster and with greater accuracy. However, while the beads are stable and reliable, certain care should be taken when using them.
Keeping your microspheres protected from cumulative light exposure
Microspheres are dyed when placed in an organic solution containing two or three fluorescent dyes. In this organic solution, the microspheres swell, allowing the dyes to diffuse into the microsphere. When the microspheres are washed, they shrink to their original size as the dyes become trapped within the microsphere. This enables Luminex to make 500 different variations of beads with each having a unique color. Each batch is assigned a number from 1 to 500, which serves to identify a bead’s region or bead ID. When the dyes are excited by the red laser of an xMAP system, each bead can be identified by the different emission peaks of the dye combination it contains. Each instrument can identify all 100 MicroPlex beads but only the FLEXMAP 3D® and xMAP INTELLIFLEX® can read all 500 regions.
The three dyes used for bead identification are light-sensitive, meaning that four to six hours of intense cumulative light exposure may result in misclassification where beads start collecting outside their designated regions on the bead map. Photobleaching of the internal dyes is irreversible, and microspheres must be discarded if this occurs. Therefore, you should always protect xMAP beads from prolonged light exposure during storage and incubations in assays.
How the bead map or doublet discriminator can benefit your routine troubleshooting
While using an xMAP flow-based instrument, how the microspheres appear in their regions on the bead map can reveal if the assay is running properly or having issues. For example, if the microspheres appear as a diagonal streak from lower left to upper right through its assigned region (see symptom list below), this may be a sign of agglutination (or the clumping) of the beads. The effect of agglutination may also be seen on the doublet discriminator (DD) plot where a peak to the right of the upper gate appears.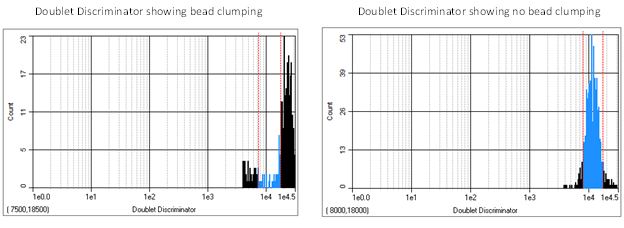
There are several causes for bead clumping, such as the cross-linking of beads during coupling (when highly hydrophobic molecules adhere to the beads), if the beads were not thoroughly vortexed and/or sonicated before assay use, or the need to include detergents and blocking agents in the bead storage and assay buffers.
If you are seeing issues with bead classification (not correctly identifying the beads in your assay), it is best to (1) ensure you selected the correct bead region in the software’s protocol, and (2) confirm the system had a successful calibration/verification to ensure the system is functioning properly.
You can use the xMAP verification microspheres to check the success of the system calibration. If there is a problem with your kit results, ensuring the system has passed calibration and verification can help you determine if the problem is a hardware issue. You may also include MagPlex® Monitoring Microspheres in your assay’s bead mix, which are magnetic polystyrene beads that aid in monitoring assay and instrument performance. These beads can help you troubleshoot if it is an assay or instrument issue that is the cause of unexpected results with median fluorescent intensity (MFI) and bead classification. Below are some additional examples and tips that can be applied to troubleshooting the Luminex® 200™, FLEXMAP 3D®, and xMAP INTELLIFLEX instruments:
Troubleshooting Acquisition Problems
Note that while these images may appear different in xPONENT® and xMAP INTELLIFLEX® software, the concepts of how they appear, and the problems and solutions they represent, are still the same.
| Symptom |
Possible Problem |
Solution |
| xMAP® microspheres properly classified.

|
Not a problem. |
No solution is required |
| xMAP® microspheres classify as too high.

|
You may be using photobleached calibration microspheres. |
Replace the calibration microspheres with a fresh batch if due to calibration beads. To avoid photobleaching, protect your microspheres from light. |
| xMAP® microspheres hit the lower right region.

|
You may be using photobleached xMAP® microspheres. |
Replace the microspheres with a fresh batch. To avoid photobleaching, protect your microspheres from light. |
| Beads appear scattered.

|
There is air in the system. |
Verify sample probe height. Run three Prime commands, two Alcohol Flush commands, and then run three Wash commands with distilled water. |
| Beads appear scattered.
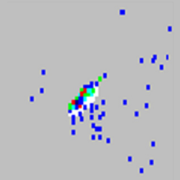
|
The sheath fluid is empty. |
Ensure there is sheath fluid in the sheath container. Prime the system until all air is out of the system. |
| Microspheres appear as a long diagonal line.
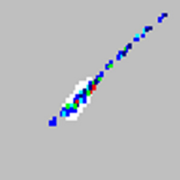
|
The xMAP® microspheres have agglutinated. |
Add additional detergent to the assay buffer. For example, add 0.2% to 0.1% Tween-20, Triton X100, or SDS. |
| Microspheres appear in an arrowhead pattern.
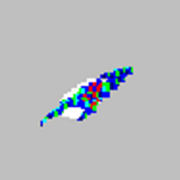
|
The assay buffer or solvent is incompatible. |
Contact Luminex Technical Support for a list of incompatible solvents. If the solvent you are using is listed, switch solvents. |
| Microspheres appear in an arrowhead pattern.

|
You are using incompatible sheath fluid. |
Use only xMAP® Sheath Fluid PLUS for your xMAP® flow-based instruments. Other fluids may cause damage and may void your warranty. |
Want to learn more about how to develop your own xMAP assay? Check out the xMAP Cookbook to learn the best practices.
Download now
Need an xMAP assay but don’t have time, bandwidth, or resources? Trust our experts in the LuminexPLORE Lab to do the work for you!
Meet the experts
About the Author
Stephen Angeloni, PhD, Sr. Field Application Scientist, Luminex
 Dr. Angeloni received his PhD in Biochemistry from Virginia Polytechnic Inst. and State University. While he has been at Luminex for 12 years, before joining Luminex he had over 30 years of research and industry experience with the development of a wide variety of biochemical, genetic, proteomic, immunology, microscopy, cellular and molecular biology assays. These technologies were applied to studying genetic and environmental factors contributing to the susceptibility or resistance to a number of infectious and non-infectious diseases. This includes studies on disease mechanisms or treatments in the areas of endocrinology, cancer, obesity, diabetes and the development of DNA vaccines. These research efforts employed cellular, mouse and non-human primate model systems. This diversified experience has been applied to developing and supporting commercial applications for cellular genetic engineering, bioinformatic data analysis as well the development of genomic and proteomic assay platforms for research and diagnostics. This experience is now available for supporting the development of several applications on the Luminex xMAP platform.
Dr. Angeloni received his PhD in Biochemistry from Virginia Polytechnic Inst. and State University. While he has been at Luminex for 12 years, before joining Luminex he had over 30 years of research and industry experience with the development of a wide variety of biochemical, genetic, proteomic, immunology, microscopy, cellular and molecular biology assays. These technologies were applied to studying genetic and environmental factors contributing to the susceptibility or resistance to a number of infectious and non-infectious diseases. This includes studies on disease mechanisms or treatments in the areas of endocrinology, cancer, obesity, diabetes and the development of DNA vaccines. These research efforts employed cellular, mouse and non-human primate model systems. This diversified experience has been applied to developing and supporting commercial applications for cellular genetic engineering, bioinformatic data analysis as well the development of genomic and proteomic assay platforms for research and diagnostics. This experience is now available for supporting the development of several applications on the Luminex xMAP platform.













 Dr. Angeloni received his PhD in Biochemistry from Virginia Polytechnic Inst. and State University. While he has been at Luminex for 12 years, before joining Luminex he had over 30 years of research and industry experience with the development of a wide variety of biochemical, genetic, proteomic, immunology, microscopy, cellular and molecular biology assays. These technologies were applied to studying genetic and environmental factors contributing to the susceptibility or resistance to a number of infectious and non-infectious diseases. This includes studies on disease mechanisms or treatments in the areas of endocrinology, cancer, obesity, diabetes and the development of DNA vaccines. These research efforts employed cellular, mouse and non-human primate model systems. This diversified experience has been applied to developing and supporting commercial applications for cellular genetic engineering, bioinformatic data analysis as well the development of genomic and proteomic assay platforms for research and diagnostics. This experience is now available for supporting the development of several applications on the Luminex xMAP platform.
Dr. Angeloni received his PhD in Biochemistry from Virginia Polytechnic Inst. and State University. While he has been at Luminex for 12 years, before joining Luminex he had over 30 years of research and industry experience with the development of a wide variety of biochemical, genetic, proteomic, immunology, microscopy, cellular and molecular biology assays. These technologies were applied to studying genetic and environmental factors contributing to the susceptibility or resistance to a number of infectious and non-infectious diseases. This includes studies on disease mechanisms or treatments in the areas of endocrinology, cancer, obesity, diabetes and the development of DNA vaccines. These research efforts employed cellular, mouse and non-human primate model systems. This diversified experience has been applied to developing and supporting commercial applications for cellular genetic engineering, bioinformatic data analysis as well the development of genomic and proteomic assay platforms for research and diagnostics. This experience is now available for supporting the development of several applications on the Luminex xMAP platform.









