Multiplex Immunoassays Enable Evaluation of GPCR-Antibody Binding
By Chris Haake
With information from a recent scientific study, this new resource can help researchers perform better analyses of their own GPCR targets
If your work involves G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), this new white paper from Luminex could show you how to generate more useful results in your experimental workflows. Need something quicker? We’ve got you covered with some key highlights.
GPCR Basics
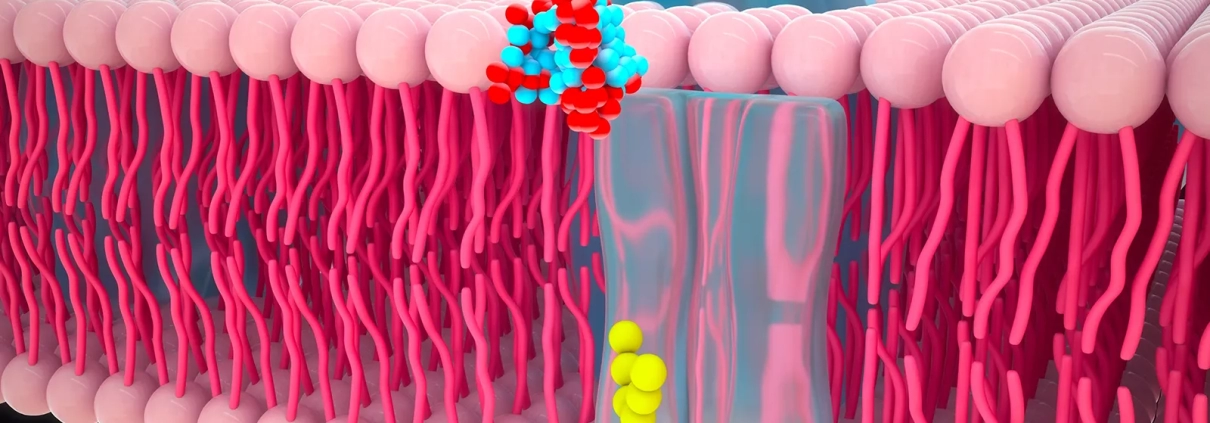
GPCRs are the largest family of membrane proteins that bind to extracellular molecules, making them an attractive target for drug development. Antibodies are generally considered the most viable therapeutic type because of their binding specificity for GPCRs. However, despite this potential, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration has only approved two antibodies that bind to GPCRs.
Antibody Binding
One of the challenges in developing GPCR-binding antibodies as therapeutic candidates is making sure those binding mechanisms are reliable and reproducible. This requires extensive testing to understand how antibodies interact with GPCRs to minimize cross-reactivity and maximize target binding. For the best results, scientists need a technology that provides highly multiplexed results, allowing for the query of dozens or even hundreds of analytes at a time.
xMAP® Technology
Luminex’s xMAP Technology enables users to perform multiplex bead-based immunoassays. In GPCR studies, multiplexing enables scientists to investigate numerous characteristics of antibody binding for target molecules. Because reactions occur in suspension rather than on a plate, protein conformation tends to be more representative of native biology. This is particularly important for GPCRs, which tend to lose their natural shape during sample purification.
The Suspension Bead Assay
Scientists at the School of Engineering Sciences in Chemistry at KTH Royal Institute of Technology recently developed the suspension bead assay: a tool for quantifying antibody binding to GPCRs. The assay, which incorporates xMAP Technology, was designed to monitor interactions between receptor activity-modifying proteins and GPCRs. It can also measure GPCR expression in the same workflow. Researchers tested the assay on 407 polyclonal antibodies against 215 dual epitope-tagged GPCR constructs from a human embryonic kidney cell line. Their analysis found that 248 antibodies recognized only their intended GPCR target while many GPCRs bound to at least two antibodies. The team also developed an online interface for easy access to the data, allowing others to examine antibody-GPCR interactions. The resource contains information about GPCR expression, antibody binding dynamics to GPCRs, and antibody selectivity to specific GPCR subfamilies.